Day 1 and 2 - Astronomy

Earth
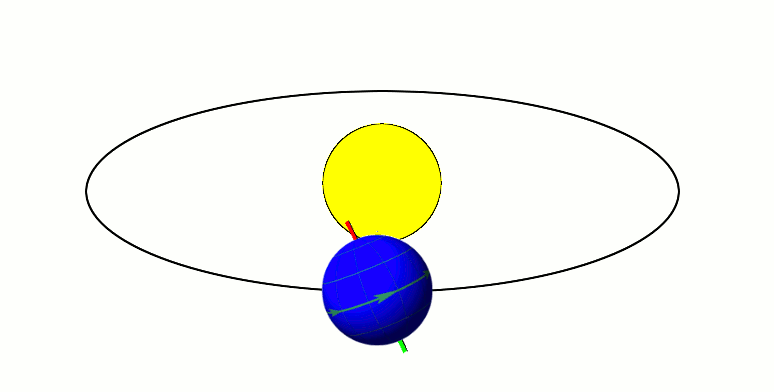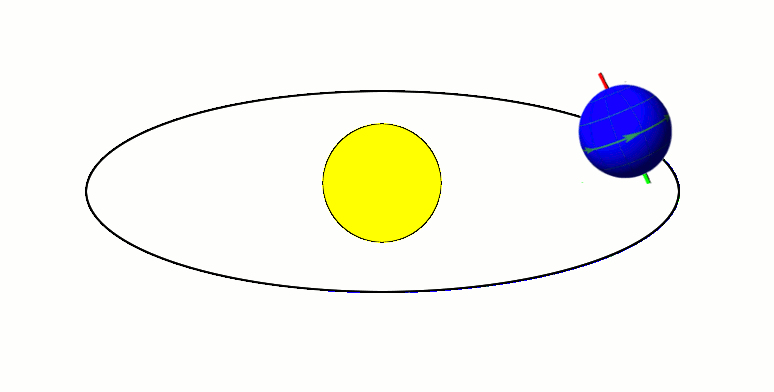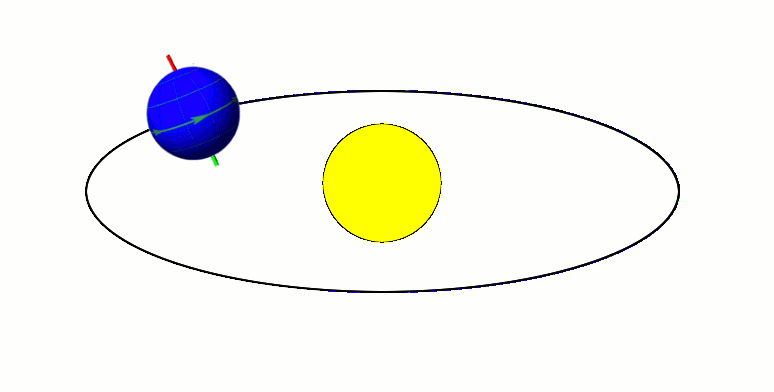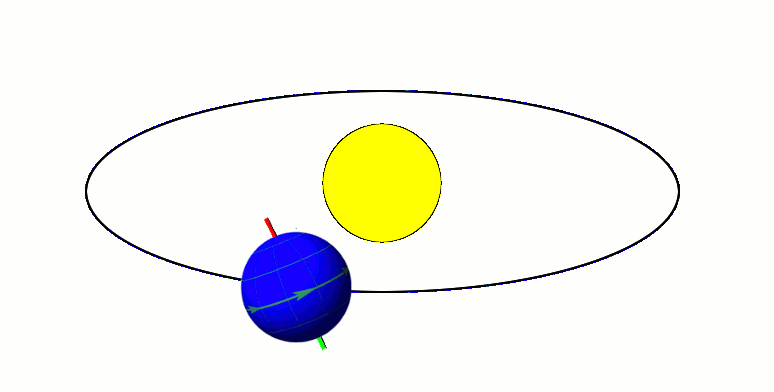
Now we will talk about how Earth moves around in space, and results of this movement.
 Tfr000 (talk) 16:54, 2 April 2012 (UTC) / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)
Tfr000 (talk) 16:54, 2 April 2012 (UTC) / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/3.0)
Earth has two types of rotations. It orbits around the sun and spins on its axis.
 Maulor / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)
Maulor / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)
Earth is constantly spinning. It spins around an imaginary line called the axis. As the Earth spins, part of it is shadowed. As the Earth spins about its axis, you will enter and exit the shadowed part of the Earth. This is the reason for day and night.
 NASA Space Place / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)
NASA Space Place / CC BY-SA (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0)
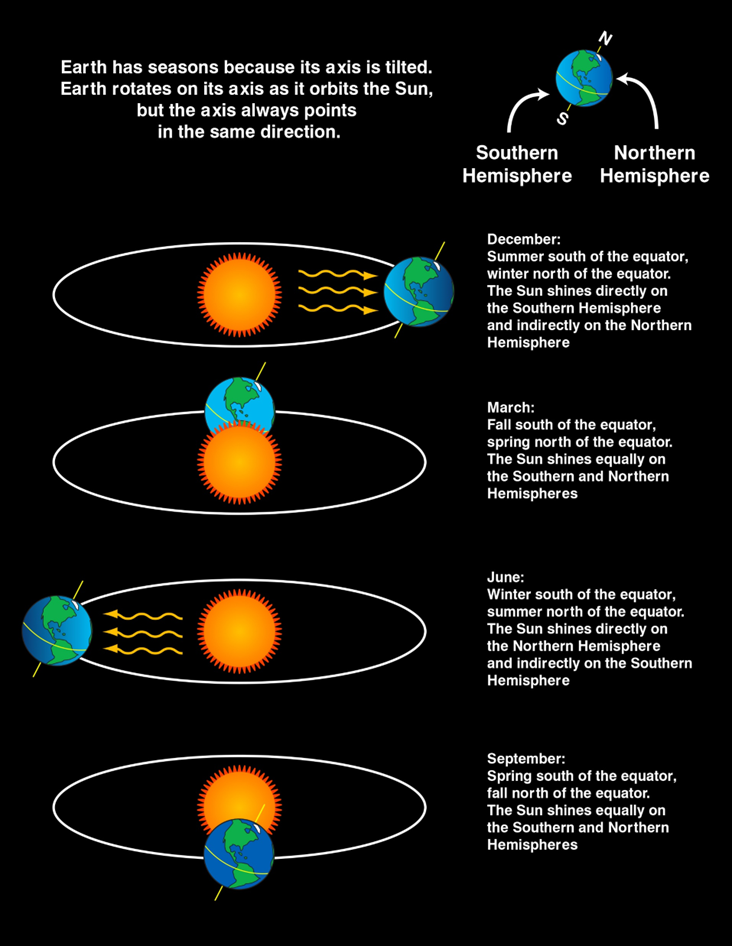
As Earth orbits the sun, the way its axis is tilted, it has one hemisphere closer to the sun than the other. This causes one hemisphere to be in the sun more than the other, and it receives more direct sunlight than the other, causing the seasons. In summer, your hemisphere is tilted toward the sun, and in winter, it is tilted away from it. Someone in the US lives in the Northern hemisphere, and someone in Australia lives in the Southern Hemisphere.
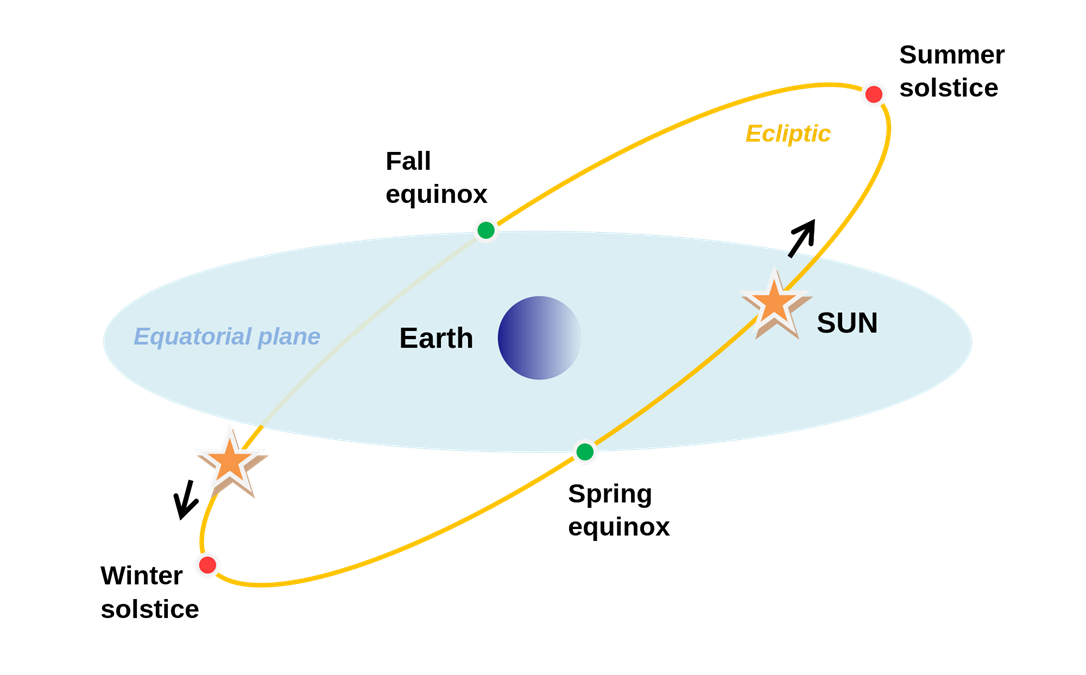
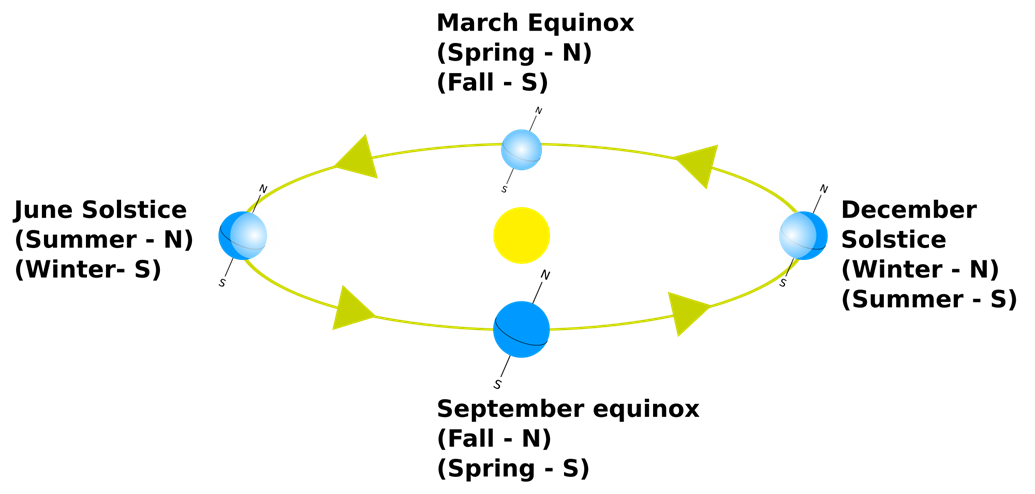
The fact that the axis is tilted means that the sun is not always directly over the equator. It is only over the equator twice a year. When this happens, it is an equinox. During an equinox, the length of day and night is the same around the world. When the sun is as far north or south of the equator as possible, it is a solstice. During a solstice, the hemisphere you’re in is experiencing either the longest day of the year or the longest night.