Day 8 - Mirrors

Before we learn about different types of mirrors we will learn some terminologies.
Upright image
An image is upright if the image is oriented in the same direction as the object. For example when you look into a household mirror the image of the body is in the same upright direction as you.
 Image attribution - AntanO/ CC BY-SA 4.0
Image attribution - AntanO/ CC BY-SA 4.0
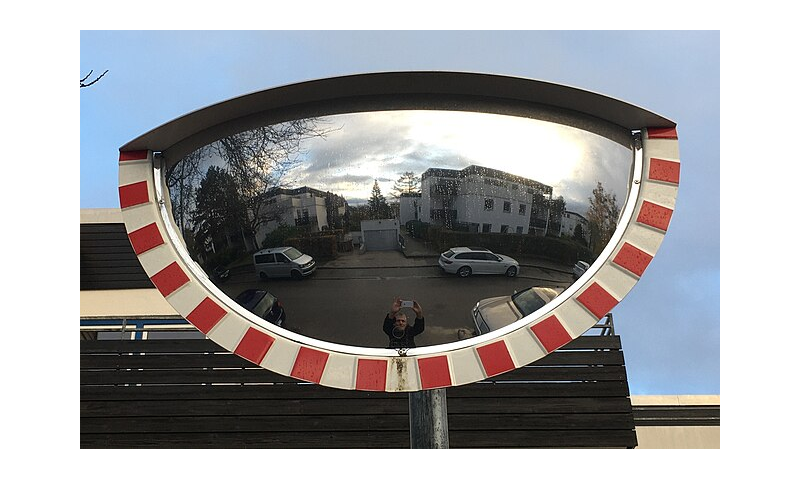
Inverted image
When you look into a mirror and the object appears inverted then it is said to create an inverted image.
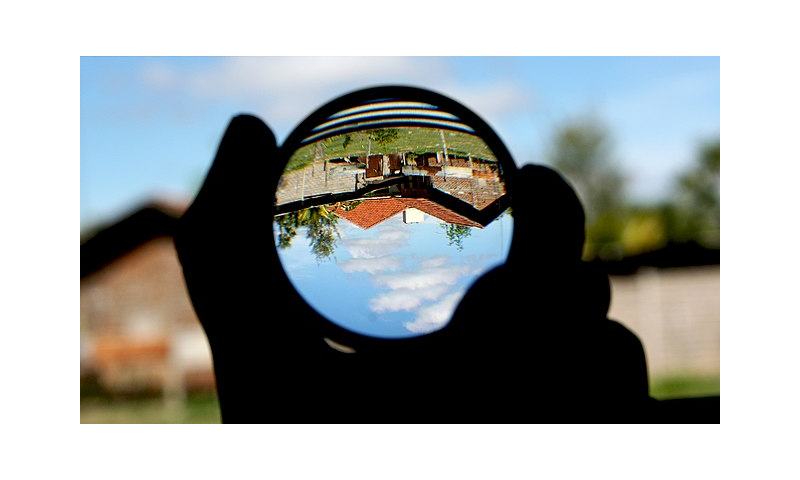 Image attribution - Cgs/ CC BY-SA 3.0
Image attribution - Cgs/ CC BY-SA 3.0
Real image
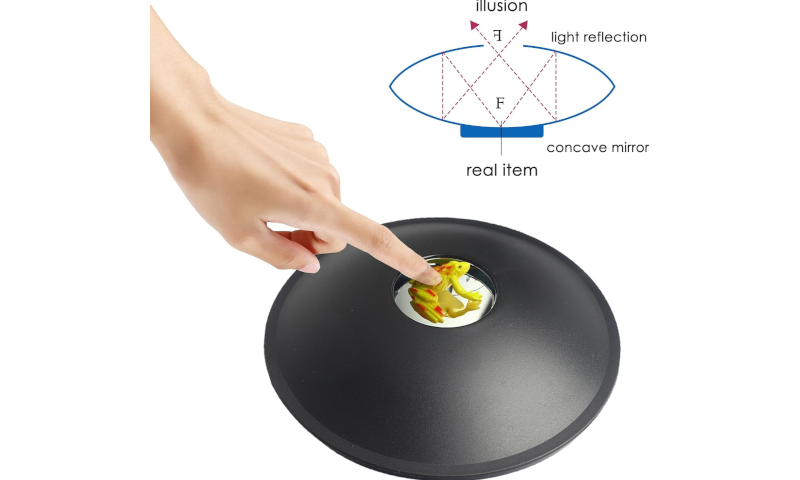
In optics image is defined as the collection of focus points of light reflected by the mirror. In some mirrors
the light rays will focus in front of the mirror creating a real image. For example a mirascope projects a 3D
image of the object that is placed inside two curved mirrors.
Virtual image
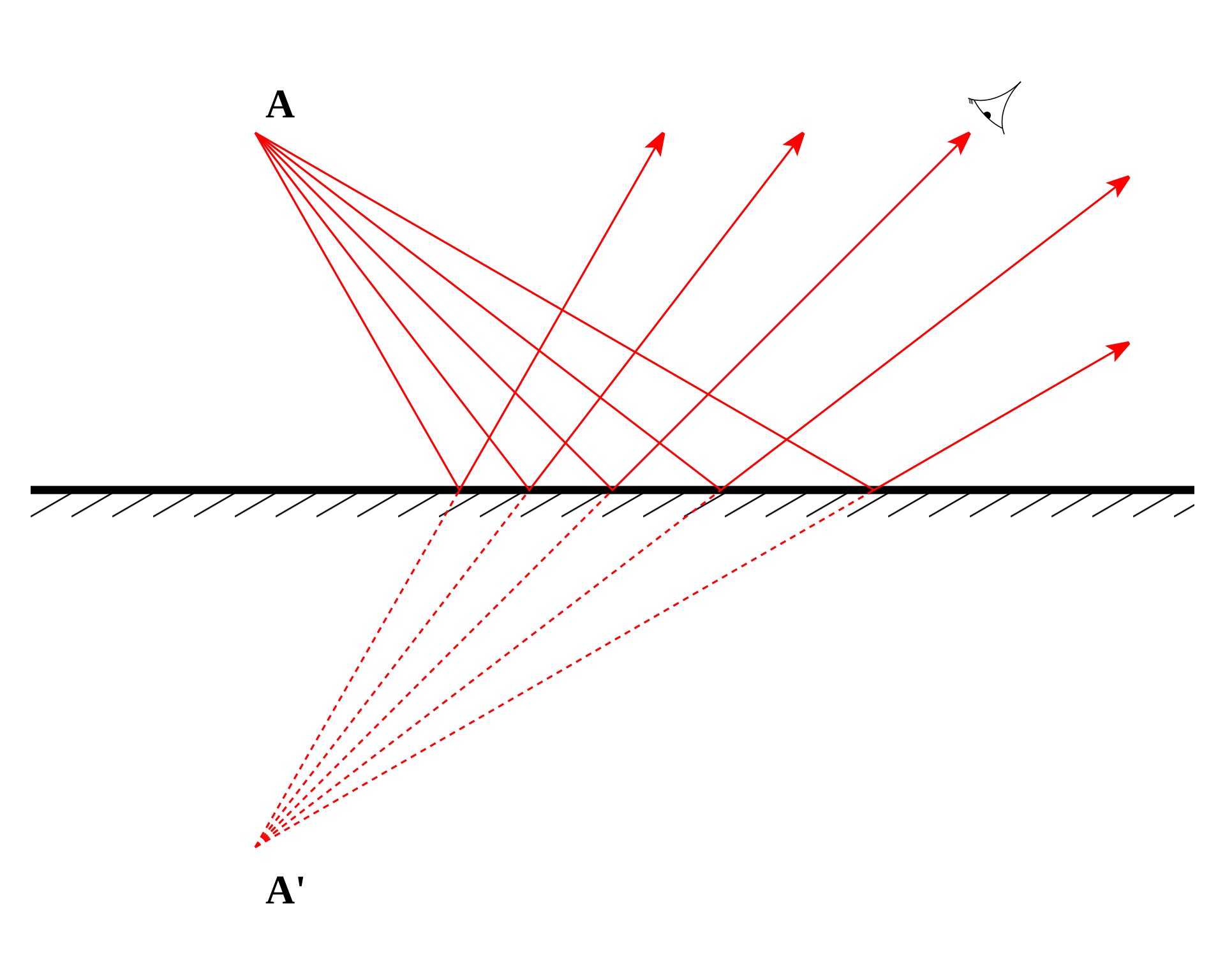
A virtual image is a collection of focus points made by extensions of diverging rays. This is why when you look into the mirror you appear to be behind the mirror.
Mirror image
When you look in the mirror why does your left side appear to be on the right side and the right side on the left. Unlike the inverted images mirror image is not caused by the property of the mirror itself, but by our perception of the image. Let’s say you look in the mirror facing north. The image on the mirror appears to be facing south. Our brain perceives this as another person standing in front of us and sees the left hand in the image as the right hand and the right hand as left hand. The mirror does not flip the image from left to right. But it flips it front to back. This phenomenon is called lateral inversion.
This effect is especially pronounced when you look at alphabets. If you hold a piece of paper with a word in it you will see the word correctly. Now if you flip the paper and look at the word from the back side of the paper, it will appear differently. The impression that you will see if the same impression you will see when you lod the piece of paper in front of the mirror. The mirror flips the image front to back. So it produces the same effect as looking at the word from the back side of the paper.
Types of mirrors
There are three commonly used types of mirrors - plane, convex or concave. Following table provides a comparison of the optical properties of these mirrors.
| Plane | Concave | Convex | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Image type | Virtual | Real or Virtual | Virtual |
| Image orientation | Upright | Upright or Inverted | Upright |
| Image height | Same as object | Smaller or larger than the object | Smaller than the object |
| Image distance | Same as object | Closer or farther from the object | Farther |